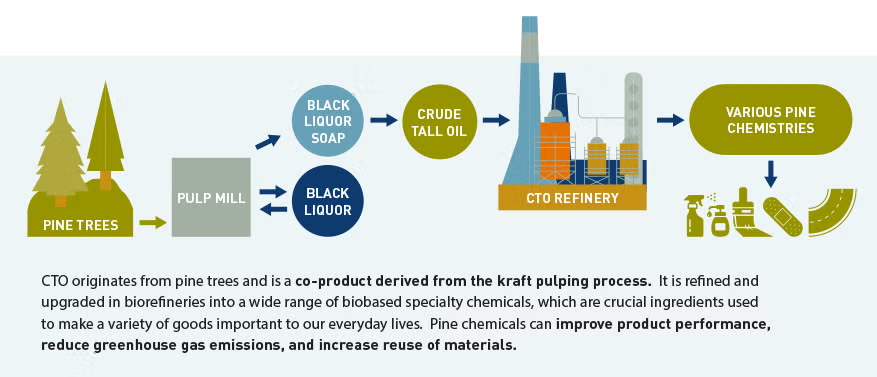
Pine chemistry refers to the co-products derived from the papermaking process that are upgraded into crucial ingredients used in a variety of goods important to our everyday lives.
Pine Chemistry
Pine Chemistry: A Chemistry with Environmental Benefits
Pine Chemistry Facts
- Pine chemistry has been around for approximately 100 years and is a long-standing example of bio-based chemistry that utilizes natural, renewable products from pine trees as raw materials.
- The industry directly contributes to the US economy with almost $2 billion in shipments and employs almost 2,000 workers (2011).
- Crude tall oil (CTO) is a prominent example of pine chemistry, and CTO refining is at the heart of a well-functioning bioeconomy.
- Crude tall oil (CTO) is a key pine chemical used to make many of the products that are important to our everyday lives. CTO can be further distilled into other pine chemicals such as heads, pitch, distilled tall oil (DTO), tall oil fatty acid (TOFA), tall oil rosin ester (TORE) and tall oil rosin (TOR).
- CTO can also be used as a feedstock in the production of biodiesel, often referred to as renewable fuel or advanced biofuel.
- The global availability of CTO will increase from 1.85 million tonnes per year in the year 2019 to 2.26 million tonnes per year in 2030. This increase is due to current and future softwood kraft pulp capacity expansions.
- Demand for CTO in bio-chemicals will grow from 1.48 million tonnes per year in 2019 to 1.56 million tonnes per year in 2030.
- Demand for CTO based biofuels for transportation will increase from 0.32 million tonnes per year in 2019 to 0.88 million tonnes per year in 2030.
- Project a growing deficit in the global CTO availability of 0.6 % in 2020 to 8% in 2030, due to increased biofuels demand.